What is the cloud and what are its pros and cons for your business?
- June 25
- 6 min

In the world of software product development, the integration of software development and IT operations has become a game-changer. DevOps, a set of practices aimed at streamlining the development process and ensuring continuous delivery of high-quality products, has gained significant recognition. However, as businesses continue to shift their application development and workloads to the cloud, a new concept called CloudOps has emerged. CloudOps, short for “cloud operations,” is designed to address the complexities that arise when managing cloud-based infrastructure.
In this article, we will explore what CloudOps entails, its benefits for organizations, and the key considerations to keep in mind when implementing CloudOps within your enterprise. So, let’s dive into the world of CloudOps and unlock its transformative potential.
CloudOps, also known as cloud operations, encompasses a range of methodologies and best practices that facilitate seamless collaboration among teams to ensure the continuous availability and optimal performance of cloud-native applications. At its core, CloudOps aims to eliminate any potential downtime associated with cloud computing.
It is a set of practices aimed at ensuring optimal performance and continuous availability of cloud-native applications. It involves managing the delivery, tuning, optimization, and performance of workloads and IT services across various cloud environments, such as multi-cloud, hybrid, data center, and edge deployments.
Similar to DevOps, which focuses on application development and delivery, CloudOps establishes standardized procedures specific to cloud-based environments. This helps streamline operational processes and ensure seamless collaboration among teams.
CloudOps has become increasingly important as organizations transition from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based solutions. In some cases, it has replaced the traditional network operations center (NOC) by assuming responsibility for monitoring, instrumenting, and managing virtual machines (VMs), containers, and cloud workloads. This collaborative approach involves developers, IT operations teams, and security personnel, aligning business objectives with technology goals.
CloudOps empowers teams to easily scale out, seamlessly work across infrastructures without the need for extensive involvement with physical servers, and enhance automation for a smoother DevOps process.
As organizations increasingly rely on the public cloud for a diverse range of applications and services, the demand for CloudOps continues to grow. With the migration of workloads from data centers to cloud providers, the importance of CloudOps becomes even more pronounced. DevOps and CloudOps teams can coexist and collaborate, sharing best practices that result in numerous benefits, including:
Improved efficiency and utilization of cloud resources: CloudOps enables organizations to optimize resource allocation, ensuring that cloud resources are used efficiently and effectively. This leads to cost savings and maximized performance.
Growth of agile work environment for cloud workloads: By embracing CloudOps principles, organizations can foster an agile work environment that promotes flexibility, adaptability, and rapid iteration. This allows for faster development and deployment of cloud-based workloads.
Automation of security and availability processes for 24/7 operations: CloudOps emphasizes the automation of critical processes such as security and availability. By automating these tasks, organizations can ensure continuous operations, reduce vulnerabilities, and provide a seamless user experience around the clock.
Improved customer user experience: With CloudOps, organizations can deliver better user experiences by leveraging the scalability, reliability, and performance capabilities of the cloud. This results in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Lowered overall costs of delivering cloud services: CloudOps enables organizations to optimize their cloud infrastructure, leading to cost reductions. By managing resources effectively and leveraging automated processes, organizations can minimize wastage and control expenses.
Enhanced productivity of teams working with migrated applications: CloudOps streamlines workflows and provides teams with the tools and processes needed to effectively manage and maintain cloud-based applications. This enhances productivity, collaboration, and overall team performance.
To embark on the CloudOps journey, it is essential to have a robust cloud management platform that seamlessly integrates the capabilities of all instances and resources within your infrastructure. A consolidated dashboard acts as a powerful tool, enabling cloud administrators to execute actions across their entire multi-cloud environment.
With a comprehensive view of their organization’s environment, teams can gain deeper insights into performance issues, deploy services consistently across clouds, and efficiently implement maintenance and security updates.
Implementing proper governance policies is also crucial for organizations with cloud infrastructure. These policies can be tailored to address technology- or business-oriented requirements, such as setting limits on machine provisioning or capping hardware usage.
CloudOps represents the future of cloud management. As applications migrate to the cloud, the complexity associated with managing legacy servers, databases, and additional platforms persists in the environment. Moreover, compliance becomes more intricate as teams adopt various services from multiple vendors. In this context, CloudOps plays an increasingly vital role in ensuring the success of organizations running applications in the cloud.
Integral to CloudOps is the use of cloud management platform tools. These tools assist in managing cloud services, provisioning resources, and automating processes to help achieve team goals. Additionally, conducting a thorough evaluation as a team is necessary to identify areas for improvement and ensure continuous operation with minimal downtime.
Testing and automation are key components of this process, but it is equally important to identify the most suitable workflows for testing before automating them. Not every test will provide valuable insights, so having parameters and tools in place to spot and resolve issues quickly is essential.
By focusing on the goal of continuous operation, teams can determine which system failures are most likely to cause downtime or disruptions and implement testing approaches that address these issues. Automation of these critical tests can greatly enhance operational efficiency.
Once the workflow is established, metrics and monitoring tools become invaluable. These tools help teams swiftly identify and flag issues by automatically collecting and analyzing large amounts of data. With precise issue detection, teams can create targeted, automated workflows to resolve problems efficiently.
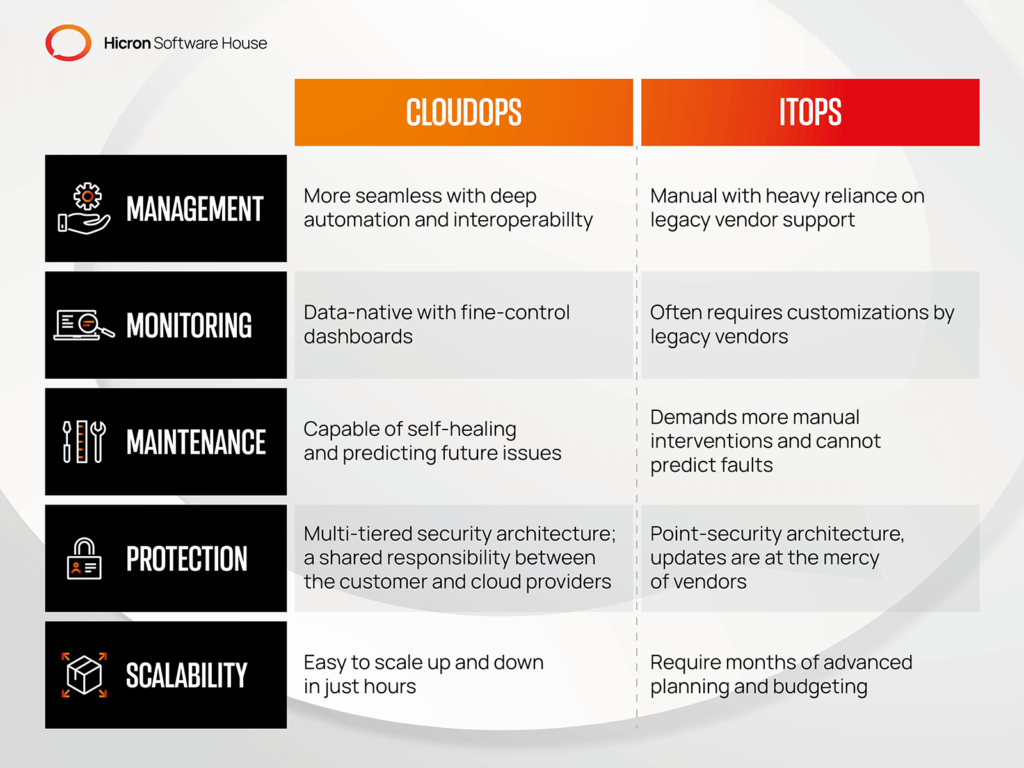
CloudOps is often mistakenly viewed as a mere continuation or evolution of ITOps. However, this assumption disregards the distinct skills and technologies associated with each discipline.
Enterprises deploying cloud-based applications are often surprised to find that CloudOps represents something entirely new.
It introduces novel processing and work streams, utilizes different technologies and tools, and requires a fresh set of skills to effectively manage ongoing cloud-based systems.
Now, let’s explore the distinctive aspects that make CloudOps both unique and indispensable:
Virtualized Infrastructure: Unlike traditional ITOps, CloudOps relies on virtualization, eliminating the need for physical servers. Cloud administrators must rely on the cloud provider’s native tools to identify and resolve issues with virtual servers that exist solely in the memory of server clusters. The days of troubleshooting hardware with screwdrivers and wrenches are replaced by leveraging cloud-native tools.
Ops Management Tools: To navigate the increased complexity of CloudOps, it is crucial to adopt effective ops management tools. As IT environments transition from complexity to distributed complexity, abstracting oneself from the intricacies becomes essential. Without proper abstraction, organizations may reach a tipping point where the number of systems surpasses their operational tracking capacity. This can result in compromised service, user impact, and delays in issue resolution.
Proactive Operations: CloudOps emphasizes a proactive approach rather than a reactive one. Identifying issues as they occur and predicting potential problems before they manifest is pivotal. For instance, automatically migrating data from one storage system to another when performance concerns arise or blocking IP addresses attempting to compromise system security. These activities are driven by continuous data gathering, analysis of patterns, and automated responses.
By recognizing the distinctive attributes of CloudOps, organizations can adapt to the demands of managing cloud-based applications more effectively. Embracing virtualized infrastructure, leveraging ops management tools, and adopting a proactive mindset are key elements in achieving operational excellence in the cloud.
Drawing from the best practices and optimization techniques of DevOps, the CloudOps team works diligently to ensure the high availability and dependable access of your company’s cloud offerings.
The primary objective of CloudOps is to establish focused and vigilant oversight over your cloud operations. With the cloud’s vastness, complexity, and rapid pace, lacking proper cloud operations can lead to difficulties. However, once you master it, you gain the ability to:
Deliver cloud services and infrastructure: CloudOps enables you to effectively provide and maintain cloud services and infrastructure, ensuring smooth operations for your users.
Optimize performance: By implementing CloudOps, you can fine-tune the performance of your cloud-based solutions, maximizing efficiency and responsiveness.
Ensure universal accessibility: CloudOps ensures that your services are accessible regardless of the platform used to access the cloud, offering seamless experiences for users across various devices.
Maintain industry standards and compliance: CloudOps incorporates necessary measures to adhere to industry standards and comply with regulatory requirements, ensuring data security and privacy.
Automate services and configuration management: Through automation, CloudOps streamlines processes, allowing for efficient service deployment, scaling, and configuration management.
Establish reliable disaster recovery: CloudOps puts robust disaster recovery mechanisms in place, safeguarding your data and applications against potential disruptions or outages.
Meet service level agreements (SLAs): CloudOps prioritizes meeting SLAs, ensuring that your cloud services consistently meet agreed-upon performance and uptime targets.
Ensure cloud service security and availability: CloudOps places a strong emphasis on security, implementing measures to keep your cloud services protected and available to authorized users.
By embracing CloudOps, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of the cloud while optimizing performance, maintaining compliance, and providing reliable and secure services for their users.

CloudOps encompasses a wide range of functions, including software development, IT operations, security, and more. Its primary objective is to unify these functions within a cloud architecture, enhancing accessibility, availability, and functionality.
In the realm of CloudOps, there is ongoing discourse surrounding its relationship with DevOps. While CloudOps draws upon DevOps best practices, it specifically applies them within a cloud-based framework.
This integration enables the establishment of a team-oriented approach to continuous operations, optimizing workloads and services.
In the context of CloudOps, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) focuses on change management and prioritizes quality and reliability. SREs play a crucial role in monitoring end-user performance stability and take ownership of meeting Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for applications. Similar to DevOps, in a CloudOps environment, SREs facilitate collaboration between cloud development teams and operations teams, ensuring reliability while aligning with business objectives.
By combining the strengths of DevOps with the unique requirements of cloud-based architectures, CloudOps enables organizations to achieve seamless operations, robust reliability, and the realization of their business goals.
Cloud overspending can have a significant impact on budget, with estimates suggesting that anywhere from 25% to 90% of cloud spend is wasted. While the extremes are less common, a more realistic range is around 35-40% of wasted spend.
Budget overruns further compound the issue, as enterprises often receive unexpected bills from their Cloud Service Providers (CSP) when it’s too late to make adjustments.
It’s been reported that approximately 80% of enterprises end up overspending, with half of them spending at least $1.2 million annually on public cloud services, and 13% spending $12 million or more.
Despite the financial risks, the public cloud Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) segments continue to grow at a rate of over 26% annually. Slowing down isn’t an option, but it’s essential to find ways to avoid blasting through expense forecasts – according to Gartner.
One of the challenges contributing to these financial risks is limited governance. The distributed autonomy to purchase and utilize cloud services has led to impaired visibility and governance. Cloud consumption happening in the shadows has likely exacerbated cost-related issues and certainly poses security and compliance risks.
Speaking of security, while public cloud platforms are not inherently insecure, ensuring appropriate configuration for each cloud resource is essential to maintain security.
According to the 2019 Cloud Security Report, a staggering 93% of enterprises express moderate to extreme concerns about cloud security.
In fact, 55% of them plan to deploy new cloud security solutions within the next 12 months to address these concerns.
Navigating the complexities of cloud spend, budget management, governance, and security is paramount for organizations as they embrace the growth and opportunities provided by the public cloud. By adopting robust cost optimization strategies, implementing effective governance frameworks, and leveraging advanced security solutions, enterprises can mitigate risks, maximize value, and thrive in the cloud environment.
When implemented correctly, CloudOps offers a highly efficient method to deliver cloud services with improved performance and effectiveness across diverse cloud platforms. By leveraging DevOps best practices, CloudOps has the potential to enhance security measures, streamline workflows, automate processes, and enable rapid deployment to customers. By adopting a focused CloudOps strategy, companies can reap several key benefits:
Cost-effectiveness
Utilizing third-party cloud infrastructure eliminates the need for significant investments in expensive hardware. This approach helps companies save on costs associated with purchasing, maintaining, and upgrading physical equipment. Additionally, expenses related to facilities, utilities, and large data center spaces can be reduced or eliminated.
Scalability and flexibility
Cloud-based services offer instant scalability, providing additional bandwidth when needed. This eliminates the requirement for manual efforts to acquire extra space or configure new hardware. Consequently, teams can focus on core business activities while the cloud handles resource scaling seamlessly.
Process automation
The cloud offers a wide range of tools that facilitate automation in various areas, including infrastructure provisioning, build creation, quality assurance testing, report generation, and more. Leveraging cloud-based automation capabilities reduces time to market, enhances efficiency, and enables teams to deliver services faster.
Enhanced security
Cloud hosting providers prioritize robust security measures to safeguard data and services from cyber threats. According to RapidScale, a survey showed that 94% of businesses experienced improved security after migrating to the cloud. This demonstrates the heightened focus on cloud security and the added protection it can provide.
Simplified backup management and disaster recovery
Cloud-based systems allow data to be stored in multiple locations, ensuring fault tolerance and offering various failover options. This simplifies backup management and enhances disaster recovery capabilities, providing greater data resilience and minimizing the risk of data loss.
Accessibility
Cloud operations can be accessed and managed from virtually anywhere using a wide range of devices across different platforms. This flexibility enables teams to collaborate effectively and perform their tasks remotely, enhancing productivity and responsiveness.
Seamless integration
Cloud environments facilitate the coexistence of applications that rely on shared services without the need for complex interconnections. This simplifies application integration processes, enabling smooth interoperability.
Continuous operations
Cloud-based software can be updated and deployed rapidly without disrupting services. This ensures that operations in the cloud remain consistently available for use, allowing for uninterrupted service delivery.
In CloudOps, two interconnected goals are paramount: achieving continuous operations and eliminating downtime. Continuous operations entail building the cloud-based system in a manner that avoids service disruptions or the need to take components offline for builds and improvements. By enabling changes without impacting availability, the objective of zero downtime can be realized.
When combined with DevOps, CloudOps unlocks enhanced speed, scalability, and productivity for your operations.
To facilitate the transition to CloudOps, consider implementing the following best practices:
Start with a small-scale approach: Identify an application that can be migrated to the cloud as a proof-of-concept for both operational and user teams. This enables stakeholders to witness the feasibility and benefits of a broader cloud migration.
Embrace infrastructure as code: Adopt the practice of storing configuration data, such as server definitions, in an infrastructure as code model. This allows for rapid expansion and deployment of new instances, ensuring scalability based on demand.
Define clear requirements for each application migration: Ensure that every application being migrated has a well-defined understanding of the necessary tools, services, and data required for successful operation. This establishes an operational blueprint of dependencies that applies to all future operations.
Achieve best agility: To enable agility in cloud computing, it is crucial to ensure that the security and governance teams are fully aligned with all aspects of the cloud environment. Collaboration and effective communication between teams are essential to avoid complications, lack of transparency, and overall disunity. Instead of imposing unnecessary restrictions, focus on clearly defining and implementing necessary guidelines that promote seamless collaboration.
Empower your users: While governance oversight and proper configuration are necessary for security and compliance, DevOps teams should have input and control over the day-to-day use of cloud resources. Enable users to self-provision their own machines or leverage auto-provisioning capabilities. This allows applications to request additional resources or scale down capacity based on usage patterns, empowering teams to optimize resource allocation efficiently.
Automate security: Mitigating security risks in the cloud can be achieved by implementing automated processes to continuously test the configuration of cloud resources. Automate security checks and establish comprehensive compliance policies across all teams to ensure consistency as your cloud footprint expands. Additionally, automate remediation processes, enabling developers to address security issues without disrupting workflows.
Implement redundancy: To achieve continuous operations and zero downtime, it is vital to implement redundancy at both the cloud provider and application layers. Cloud-based systems facilitate seamless software updates and deployments without impacting application availability. By leveraging automation and redundancy, you can ensure that critical applications remain accessible even during updates or software changes.
Streamline the change management: DevOps aims to minimize the time from idea development to product deployment, but change management processes can create bottlenecks. Foster synergy between cloud security and change management by implementing streamlined processes that support the development process. Automate change request tickets and establish an agile change management system that encourages seamless collaboration among teams.
Embrace automation: Increasing automation levels can streamline processes related to provisioning, configuration, upgrades, and repetitive tasks. By automating these tasks, resources can be redirected towards enhancing products or services, rather than being consumed by manual procedures that slow down development.
Optimize resource usage: One of the benefits of the cloud is the ability to scale resources as needed. Instead of investing in expensive hardware, leverage the cloud’s scalability. However, be mindful of unexpected maintenance costs that may arise. Optimize resource usage to ensure cost-efficiency while meeting business requirements.
Adopt a data-first approach: Manage data holistically and in a unified manner, even across different cloud platforms. Implement solutions that enable efficient data management, ensuring data integrity and accessibility throughout the cloud environment.
Develop a cloud migration strategy: Moving your business to the cloud requires a well-defined cloud migration strategy. Consider factors such as cost, security risks, management buy-in, and other relevant considerations to ensure a smooth and successful transition.
Visualize network infrastructure: Gain a comprehensive understanding of your current network infrastructure by mapping out systems and their interconnections. Documenting your network enables informed decision-making when adapting processes to cloud technologies.
Promote a culture shift: Introducing cloud computing to your organization may require a culture shift. Help management and employees transition from traditional processes to cloud-enabled practices. Emphasize how CloudOps aligns with DevOps strategies, offering increased flexibility, agility, and speed.
In the field of CloudOps, there is a diverse range of tools that organizations commonly utilize to effectively manage and maintain their cloud-based infrastructure and applications. Let’s explore some examples:
Configuration Management Tools
Ansible, Chef, and Puppet are widely used to automate the provisioning and configuration of cloud-based systems. These tools streamline the process of setting up and managing infrastructure components.
Monitoring and Logging Tools
Amazon CloudWatch, Elastic Stack, and Datadog are employed to collect and analyze performance and operational data from cloud-based environments. These tools enable proactive monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization of resources.
Container Orchestration Tools
Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, and Mesosphere help in deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications within cloud environments. These tools provide efficient orchestration capabilities, allowing for seamless deployment and resource allocation.
Security Tools
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Azure Active Directory, and Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) are essential for securing cloud-based systems. They enable granular control over user access, permissions, and authentication, ensuring robust security measures.
Automation and Scripting Tools and Languages
Python, Ruby, and PowerShell offer powerful automation and scripting capabilities for managing cloud-based environments. These tools enable the automation of repetitive tasks, simplifying operations and enhancing efficiency.
Cloud Management Platforms
AWS Management Console, Azure Portal, and Google Cloud Console serve as centralized management hubs for multiple cloud services. These platforms provide a unified interface to monitor, configure, and manage various aspects of the cloud environment.
These examples represent just a fraction of the wide array of tools available to CloudOps teams. The choice of specific tools depends on an organization’s unique requirements and the cloud services.
CloudOps has a vast array of tools from numerous vendors are available to support organizations in managing their cloud infrastructure. However, administrators face the challenge of selecting and limiting the number of tools required to maintain optimal performance and availability.
Leading public cloud providers like Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud offer their customers a comprehensive suite of CloudOps tools. These tools provide a wide range of functionalities, enabling organizations to efficiently manage and optimize their cloud environments.
Azure CloudOps is a comprehensive set of practices and processes designed to effectively manage and maintain cloud-based infrastructure and applications on the Microsoft Azure platform. Azure CloudOps teams play a crucial role in ensuring the security, availability, and performance of Azure-based systems.
The Azure CloudOps framework encompasses a range of services and features that empower organizations to efficiently manage their Azure-based systems. Some key components of Azure CloudOps include:
Azure Resource Manager (ARM): This powerful tool enables the provisioning, monitoring, and management of Azure resources using templates, ensuring consistency and efficient resource allocation.
Azure Monitor: As a real-time data and analytics service, Azure Monitor provides valuable insights into Azure-based systems through performance metrics, log data, and alerts. This enables proactive monitoring and troubleshooting for enhanced system performance.
Azure Security Center: By leveraging Azure Security Center, CloudOps teams can effectively manage the security of their Azure-based systems. This includes vulnerability management, threat protection, and actionable security recommendations to maintain a robust security posture.
Azure Automation: With Azure Automation, repetitive tasks can be automated, and Azure-based systems can be efficiently managed using scripts and runbooks. This streamlines operational processes and improves overall efficiency.
Azure DevOps: Azure DevOps offers a comprehensive suite of tools for software development and deployment, including continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines and agile project management capabilities. This facilitates seamless collaboration and efficient software delivery.
Azure Backup: Azure Backup provides a reliable cloud-based data backup and recovery solution for Azure-based systems. It ensures data resilience and allows for quick restoration in case of any unforeseen incidents or data loss.
Azure Site Recovery: Azure Site Recovery offers disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities for Azure-based systems. It provides replication and failover options, enabling organizations to maintain operations during unforeseen disruptions.
These examples represent just a fraction of the vast array of services and features available within Azure CloudOps. Organizations can tailor their CloudOps practices to meet their specific needs and leverage the full potential of Azure’s capabilities.
AWS CloudOps, which stands for Amazon Web Services Cloud Operations, encompasses a comprehensive set of practices and processes used to effectively manage and maintain cloud-based infrastructure and applications on the Amazon Web Services (AWS) platform. AWS CloudOps teams play a crucial role in ensuring the security, availability, and performance of AWS-based systems.
Within AWS CloudOps, there is a wide range of services and features available that enable seamless management and maintenance of AWS-based systems. Some key components of AWS CloudOps include:
AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): This service allows for the provisioning and management of virtual machines, providing flexible computing resources tailored to meet specific requirements.
AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS) and Simple Storage Service (S3): These storage options provide reliable and scalable storage solutions for AWS-based systems, catering to various storage needs.
AWS CloudFormation: By utilizing CloudFormation, AWS resources can be provisioned, monitored, and managed using templates. This enables consistent and efficient resource management.
Amazon CloudWatch: As a real-time data and analytics service, CloudWatch offers valuable insights into the performance of AWS-based systems. It provides performance metrics, log data, and alerts, empowering proactive monitoring and troubleshooting.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM provides robust security management for AWS-based systems, offering capabilities such as user and role management, access controls, and permissions management.
AWS Lambda: With Lambda, organizations can automate repetitive tasks and efficiently manage AWS-based systems using serverless functions. This allows for streamlined operations and improved efficiency.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Elastic Beanstalk provides a platform for deploying, running, and scaling web applications and services on AWS. It simplifies the deployment process and offers scalability options based on demand.
AWS CloudTrail: CloudTrail provides a comprehensive record of all AWS Management Console sign-in events and API calls made within an AWS account. This auditing and compliance service assists in maintaining visibility and accountability.
Customize your CloudOps practices to match your unique requirements, and make the most of AWS services to revolutionize your cloud-based systems.
Google CloudOps, also known as Google Cloud Operations, encompasses a comprehensive set of practices and processes used to effectively manage and maintain cloud-based infrastructure and applications on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). With a focus on security, availability, and performance, Google CloudOps teams play a crucial role in ensuring the success of GCP-based systems.
Within Google CloudOps, a wide range of services and features are available to facilitate the management and maintenance of GCP-based systems. Here are some notable components:
Google Compute Engine (GCE): GCE allows for the provisioning and management of virtual machines on GCP. It offers flexible computing resources that can be tailored to specific needs.
Google Cloud Storage: This service provides scalable and durable storage options for GCP-based systems. It caters to various storage requirements, ensuring data reliability and accessibility.
Google Cloud Deployment Manager: By utilizing Deployment Manager, users can provision, monitor, and manage GCP resources using templates. This simplifies resource management and ensures consistency.
Stackdriver: It is a real-time data and analytics service that provides valuable insights into the performance of GCP-based systems. It offers performance metrics, log data, and alerts, enabling proactive monitoring and troubleshooting.
Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM provides robust security management for GCP-based systems. It includes features such as user and role management, access controls, and permissions management to ensure proper data protection.
Google Cloud Functions: With Cloud Functions, organizations can automate repetitive tasks and efficiently manage GCP-based systems using serverless functions. This enhances productivity and scalability.
Kubernetes Engine: The Kubernetes Engine provides a powerful platform for deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications on GCP. It simplifies application management and enables efficient resource allocation.
Google Cloud Logging: This service offers centralized log management for GCP-based systems. It provides a consolidated view of logs, facilitating troubleshooting and analysis.
Network engineering teams can leverage proprietary tools such as Apigee or Flexera (previously known as RightScale), which offer specialized capabilities for cloud resource management. Additionally, open-source tools like Ansible or Chef are popular choices for automating configuration management, cloud provisioning, and application deployment.
The key for administrators is to carefully evaluate their specific needs and select the tools that best align with their requirements. By strategically combining tools from reputable vendors, organizations can streamline their CloudOps processes, enhance performance, and ensure high availability.
